Maths | ROC Curves
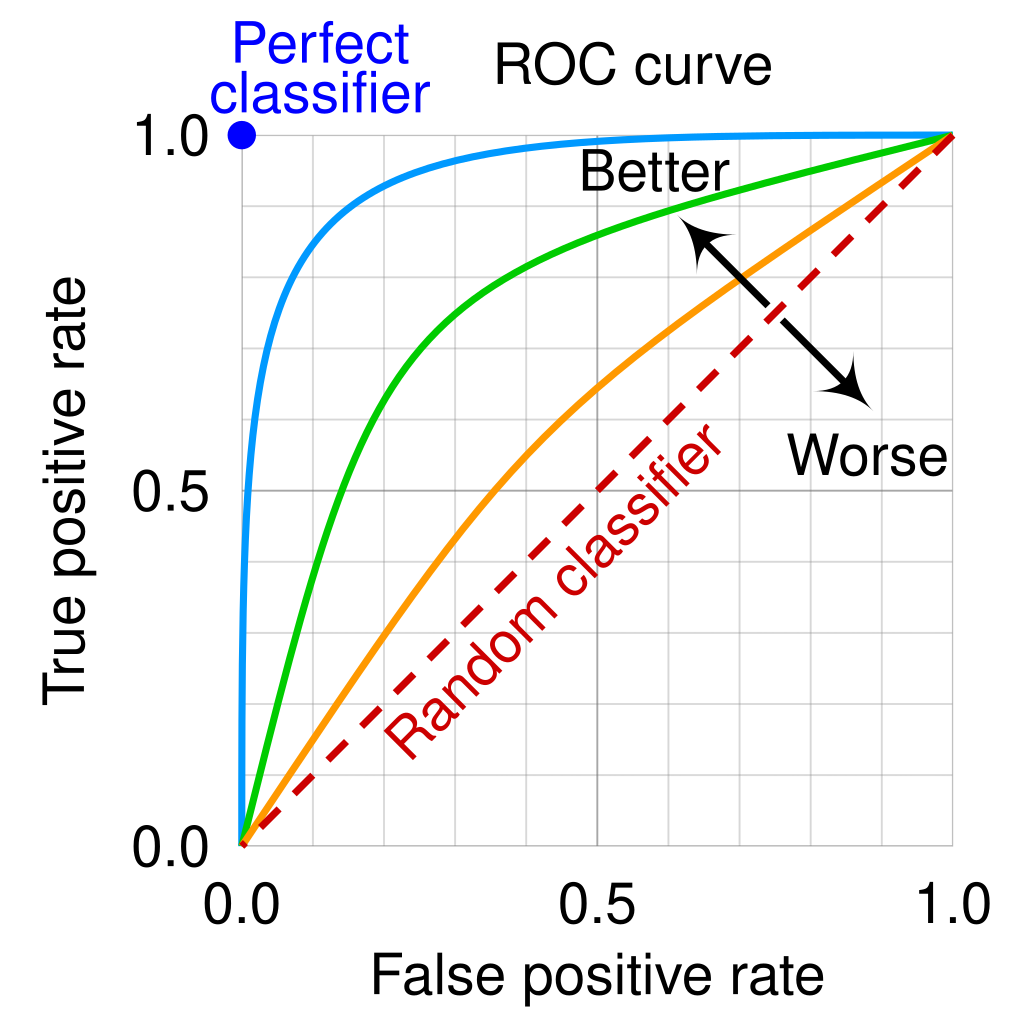
ROC curve
在訊號檢測理論中,接收者操作特徵曲線,或者叫 ROC 曲線(Receiver operating characteristic curve),是一種坐標圖式的分析工具,
- 用於選擇最佳的訊號偵測模型 、
- 捨棄次佳的模型 或者
- 在同一模型中設置最佳閾值。
在做決策時,ROC分析能不受成本/效益的影響,給出客觀中立的建議。
ROC曲線 (Receiver operating characteristic curve) 是第二次世界大戰中的發明,最初用在1941年的珍珠港事件,以偵測戰場上的日軍載具(飛機、船艦),其原理係利用雷達上的信號強弱設定閾值,以作為軍事行動的判斷依據,而發展出的信號偵測理論(Signal Detection Theory ),1950年代被應用在心理學領域。數十年來,ROC分析被用於醫學、無線電、生物學、犯罪心理學領域中,而且最近在機器學習(machine learning)和數據探勘(data mining)領域也得到了很好的發展。在醫學上,廣泛地應用在疾病的診斷,同時也被應用在流行病學、實證醫學研究、放射技術、社會科學的研究上。在臨床上可能會面對檢驗方法複雜、耗時、有侵入性、結果需要有經驗者才能準確判讀等因素,而利用ROC曲線發展出更簡易操作的替代方式,並與臨床認定的黃金標準(Gold standard)作比較,例如以癌症的切片檢查作為黃金標準,該標準將病人判定為罹癌與未罹癌,以鑑定新的診斷工具替代黃金標準的可行性。
- A receiver operating characteristic curve, orROC curve, is a graphical plot that illustrates theperformance of a binary classifier model (can be usedfor multi class classification as well) at varying thresholdvalues.
- The ROC curve is the plot of the true positive rate (TPR)against the false positive rate (FPR) at each thresholdsetting.
Terminology,
- True positive (TP)
- False positive (FP)
- True negative (TN)
- False negative (FN)
- The
true-positive rate(TPR) is also known as sensitivity or probability of detection. - The
false-positive rate(FPR) is also known as the probability of false alarm and equals (1 − specificity). ROCis also known as a relative operating characteristic curve, because it is a comparison of two operating characteristics (TPR and FPR) as the criterion changes.
在信號偵測理論中,ROC曲線是以圖像的方式呈現二分類系統(binary classifier system)在特定的分類或閾值(discrimination threshold)下的表現。
- 圖形的縱軸(y-axis)為真陽性率(true positive rate; TPR),又稱為敏感度(sensitivity);
- 橫軸(x-axis)為偽陽性率(false-posiitive rate; FPR),以1 – 特異度(specificity)表示,
而敏感度為將結果正確判斷為陽性的機率,特異度係將結果正確判斷為負向或陰性的機率。當指定一個分界點(cut-point)來區分檢驗的陽性與陰性時,這個分界點會影響到診斷工具的敏感度(sensitivity)及特異度(specificity)。在醫學上,敏感度表示有病者被判為陽性的機率,而特異度表示無病者被判為陰性的機率。在曲線上的任何一個點都會對應到一組敏感度與1-特異度,而敏感度與特異度會受到分界點移動的影響。
Each prediction result or instance of a confusion matrixrepresents one point in the ROC space.
In the field of machine learning and specifically the problem of
statistical classification, a confusion matrix, also known
as error matrix.
By adjusting the threshold used by this classifier, we canget a curve passing through (0, 0) and (1, 1). This is theROC curve of this classifier.
ROC Curve Equation
The ROC curve is based on two key metrics:
True Positive Rate (TPR), also known as Sensitivity: \[ \text{TPR} = \frac{\text{True Positives (TP)}}{\text{True Positives (TP)} + \text{False Negatives (FN)}} \]
False Positive Rate (FPR): \[ \text{FPR} = \frac{\text{False Positives (FP)}}{\text{False Positives (FP)} + \text{True Negatives (TN)}} \]
The ROC curve is a plot of TPR against FPR at various threshold settings. Each point on the ROC curve corresponds to a different threshold, showing the trade-off between sensitivity and specificity. The area under the ROC curve (AUC) quantifies the overall ability of the model to discriminate between positive and negative classes.

AUC (Area Under roc Curve)
一般情況下,這個曲線都應該處於(0, 0)和(1, 1)連線的上方。因為(0, 0)和(1, 1)連線形成的ROC曲線實際上代表的是一個隨機分類器。如果很不幸,你得到一個位於此直線下方的分類器的話,一個直觀的補救辦法就是把所有的預測結果反向,即:分類器輸出結果為正類,則最終分類的結果為負類,反之,則為正類。雖然,用ROC 曲線來表示分類器的效能很直覺好用。可是,人們總是希望有一個數值來標示分類器的好壞。於是Area Under roc Curve(AUC)就出現了。顧名思義,AUC的值就是處於ROC 曲線下方的那部分面積的大小。通常,AUC的值介於0.5到1.0之間,較大的AUC代表了較好的表現。 AUC(Area Under roc Curve)是用來度量分類模型好壞的一個標準。
ROC vs PR
The equations for the ROC (Receiver Operating Characteristic) curve and the PR (Precision-Recall) curve are derived from their respective metrics used to assess the performance of binary classifiers.
PR Curve Equation
The PR curve focuses on two different metrics:
Precision: \[ \text{Precision} = \frac{\text{True Positives (TP)}}{\text{True Positives (TP)} + \text{False Positives (FP)}} \]
Recall (which is equivalent to TPR): \[ \text{Recall} = \frac{\text{True Positives (TP)}}{\text{True Positives (TP)} + \text{False Negatives (FN)}} \]
The PR curve is a plot of Precision against Recall at various thresholds. This curve is particularly useful in scenarios where the positive class is rare or when false positives are more critical than false negatives. The area under the PR curve (AUC-PR) provides a summary measure of the model's ability to maintain precision across different levels of recall.

Summary
In summary, both curves provide valuable insights into classifier performance, but they focus on different aspects: - The ROC curve evaluates the balance between sensitivity and specificity. - The PR curve emphasizes the trade-off between precision and recall, making it more suitable for imbalanced datasets.
The ROC (Receiver Operating Characteristic) curve and the Precision-Recall (PR) curve are both essential tools for evaluating the performance of binary classification models, but they serve different purposes and are suited to different scenarios. Here are the key differences:
Key Differences Between ROC and PR Curves
- Focus on Class Distribution:
- ROC Curve: This curve plots the True Positive Rate (TPR) against the False Positive Rate (FPR) across various threshold settings. It considers both positive and negative classes equally, making it suitable for balanced datasets where both classes are important.
- PR Curve: In contrast, the PR curve focuses specifically on the positive class by plotting Precision (the proportion of true positive predictions among all positive predictions) against Recall (the proportion of actual positives correctly identified). This makes it particularly useful in scenarios with imbalanced datasets, where the positive class is rare or more critical.
- Interpretation of Metrics:
- ROC Curve: The area under the ROC curve (AUC-ROC) provides a single measure of overall model performance, indicating how well the model distinguishes between classes regardless of their distribution[3][4].
- PR Curve: The area under the PR curve (AUC-PR) reflects the model's ability to maintain high precision while capturing as many true positives as possible. It is especially informative when false positives carry significant consequences, such as in fraud detection or medical diagnoses[2][6].
- Performance Visualization:
- ROC Curve: The ROC curve can sometimes present an overly optimistic view of a model's performance in highly imbalanced datasets because it accounts for true negatives that may not be relevant in such cases[1][3].
- PR Curve: The PR curve provides a clearer picture of performance when dealing with imbalanced classes, as it directly relates to the positive class's prediction quality without being influenced by the large number of true negatives[2][6].
- Use Cases:
- ROC Curve: Best used when you want to evaluate a model's performance across different thresholds in balanced datasets or when both classes are equally important. It is also useful for comparing multiple models[3][4].
- PR Curve: More appropriate for applications where the positive class is significantly less frequent than the negative class, such as in medical testing for rare diseases or fraud detection, where maximizing precision and recall for the minority class is crucial[1][2][3].
Conclusion
In summary, while both ROC and PR curves are valuable for assessing binary classifiers, they cater to different needs based on class distribution and specific evaluation goals. ROC curves are ideal for balanced datasets, whereas PR curves excel in situations with significant class imbalance, providing deeper insights into model performance related to the positive class. Leveraging both curves can offer a comprehensive understanding of a model's strengths and weaknesses.
深入介紹及比較ROC曲線及PR曲線
- ROC Curves 適合類別平均的情況,而 PR Curves 適合於類別不平均的情況
- AUC (Area under curve) 可以當作一個判斷整體模型能力(skill)的指標
- 可以直接比較不同模型在不同Threshold下的Skill
- ROC 曲線同時考慮了正例以及負例,因此適用於評估分類器整體的效能,而 PR 曲線則專注於正例,若是在類別平均且正例及負例的判斷都重要的情況下,ROC 曲線是不錯的選擇
- 由於 ROC 曲線的 X 軸使用到了 FPR,在類別不平均的情況下(負樣本較多),使得 FPR 的增長會被稀釋,會導致 ROC 曲線呈現出過度樂觀的結果,因此在類別不平均的情況下,PR 曲線會是較好的選擇
圖解 ROC 曲線:精通 ROC 與 AUC 用法、輕鬆記熟定義
- 分類模型只會輸出機率,不會真的幫你「分類」
- 在機器學習領域的分類問題,我們通常會把分析模型稱為分類器(Classifier),好像模型會幫我們做好分類一樣,但實際上不是如此!不論是 貝氏分類器、或者羅吉斯回歸,統計模型只負責輸出機率,最後要怎麼分類是決策者的職責。認清這點,就能理解 ROC 曲線的價值了。
- 對於不同資料使用場景,決策的閾值(Threshold 或者 Cut-off)—也就是機率門檻值—將會不同,ROC 曲線的核心目標正是要呈現不同閾值會對你的決策品質造成什麼影響。
- (補充:正負樣本是針對二分類問題的真實資料而言,正樣本的意思是真實答案為正向;例如真實資料顯示有下雨;反之為負樣本,例如資料顯示實際上沒有下雨)
- 以上兩數據都是基於「決策者預測結果為正樣本」
- 我們作為決策者當然只在乎預測為正樣本的情形!
- 這則筆記前面強調過分類模型只會輸出機率,不會真的幫你分類,而分類的決策又取決於閾值(機率的門檻值),ROC 曲線的目標是要呈現不同閾值會造成什麼不同的決策品質。
- 實際上,AUC 除了在圖形上代表面積,其數據亦存在數學意義:AUC 代表隨機一個(答案為)正樣本被預測出的分數高於隨機一個(答案為)負樣本的機率。更囉唆地解釋:先隨機選一個已知答案為正的樣本,再隨機選一個已知答案為負的樣本,AUC 代表分類器預測此正樣本比此負樣本更可能為正樣本的機率。值得注意的是,AUC 的此數學意義同樣與閾值無關、不受閾值選擇限制喔!
- 一條 ROC 曲線:單一個分類器比較不同閾值的成效
- 多條 ROC 曲線:用 AUC 比較多個分類器整體表現